Objective
To verify the behavior of a non-prismatic beam
Problem Description
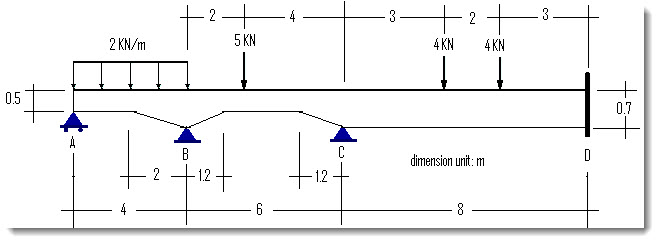
A 3-span non-prismatic continuous beam is fixed at the right end as shown below [Ref 1].
Material properties: E = 1.99948e11 N/m2, ν = 0.3
Section properties: width b = 0.1 m, heights as shown (unit: meter)
Finite Element Model
3 beam elements, then use Create > Templates > Non-Prismatic Members
Model type: 2D Frame (do not consider shear deformation)
Results
The moments at supports given by ENERCALC 3D are compared with those given in [Ref 1].
Unit: moment – KN-m
ENERCALC 3D |
[Ref 1] |
||||
Mz @ B |
Mz @ C |
Mz @ D |
Mz @ B |
Mz @ C |
Mz @ D |
-4.39 |
-4.24 |
-9.13 |
-4.28 |
-4.21 |
-9.15 |
Comments
The results given by ENERCALC 3D are close to the referenced values.
In ENERCALC 3D, the non-prismatic beam is approximated by splitting an existing beam into multiple beams (segments) to which different section properties are automatically assigned. The steps to create the model in this problem are as follows:
1. Create 3 (prismatic) beams: AB - 4 m, BC – 6m, CD – 8 m
2. Define and assign uniform and point loads on beams
3. Assign supports to A, B, C and D
4. Define and assign section to beam CD
5. Define and assign material to beams AB, BC, and CD.
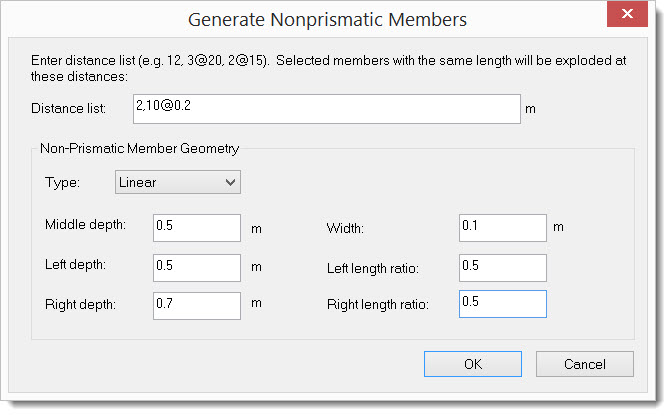
6. Select the beam AB. Run the command Create > Templates > Non-Prismatic Members. Enter the input for “Generate Nonprismatic Members” as follows. The distance list specifies how many beam segments to be used to approximate the non-prismatic beam. In our input, we use one segment for the left 2 m and 10 segments for the right 2 m haunch. More segments could be used to achieve even more accurate result. It should be pointed out that appropriate section properties are assigned to the segmented beams.
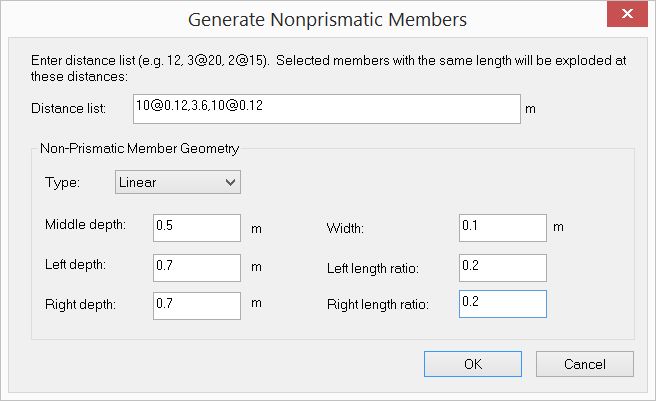
7. Select the beam BC. Run the command Create > Templates > Non-Prismatic Members. Enter the input for “Generate Nonprismatic Members” as follows.
Reference
[1]. Lin, Liu, Jiang “Structural Statics Calculation Manual”, pp 232, Building Industry Publishing House of China, 1993