There are four different structural entities to model with in ENERCALC 3D:
Nodes:
![]()
•Also known as "joints".
•Serve as points of connectivity and load transfer in a model.
•Think of a node as a beam to column connection, or a column base, or the point where chevron braces connect to a beam.
Members:

•Also known as "beams".
•One dimensional structural members that can have axial stiffness as well as biaxial flexural and shear stiffness.
•Members are useful for modeling beams, columns, braces, truss webs and chords, struts, hangers, brackets, outriggers, posts, links, etc.
Shells:
•Also known as "plates"
•Two-dimensional quadrilateral elements that have the ability to span in two directions and that have in-plane shear (racking) stiffness.
•Shells are useful for modeling masonry walls, concrete walls and floors, plywood walls, etc.
Bricks:
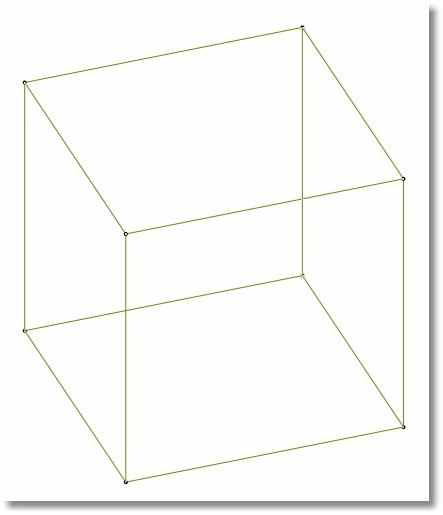
•Three dimensional solid elements defined by 8 nodes.
•Bricks are useful for modeling thick things like a massive combined footing or the face of a dam or stem of a retaining wall.
•More useful than shells in situations where the through-thickness effects have a significant role in the behavior of the element.